The Mechanics of Hybrid Vehicle Technology
Hybrid vehicles represent a significant advancement in automotive engineering, combining traditional internal combustion engines with electric propulsion systems. This integration aims to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, offering a bridge between conventional gasoline-powered cars and fully electric models. Understanding the intricate mechanics behind these vehicles reveals how they achieve their unique balance of power and environmental consideration, influencing the future of personal transport and sustainability.
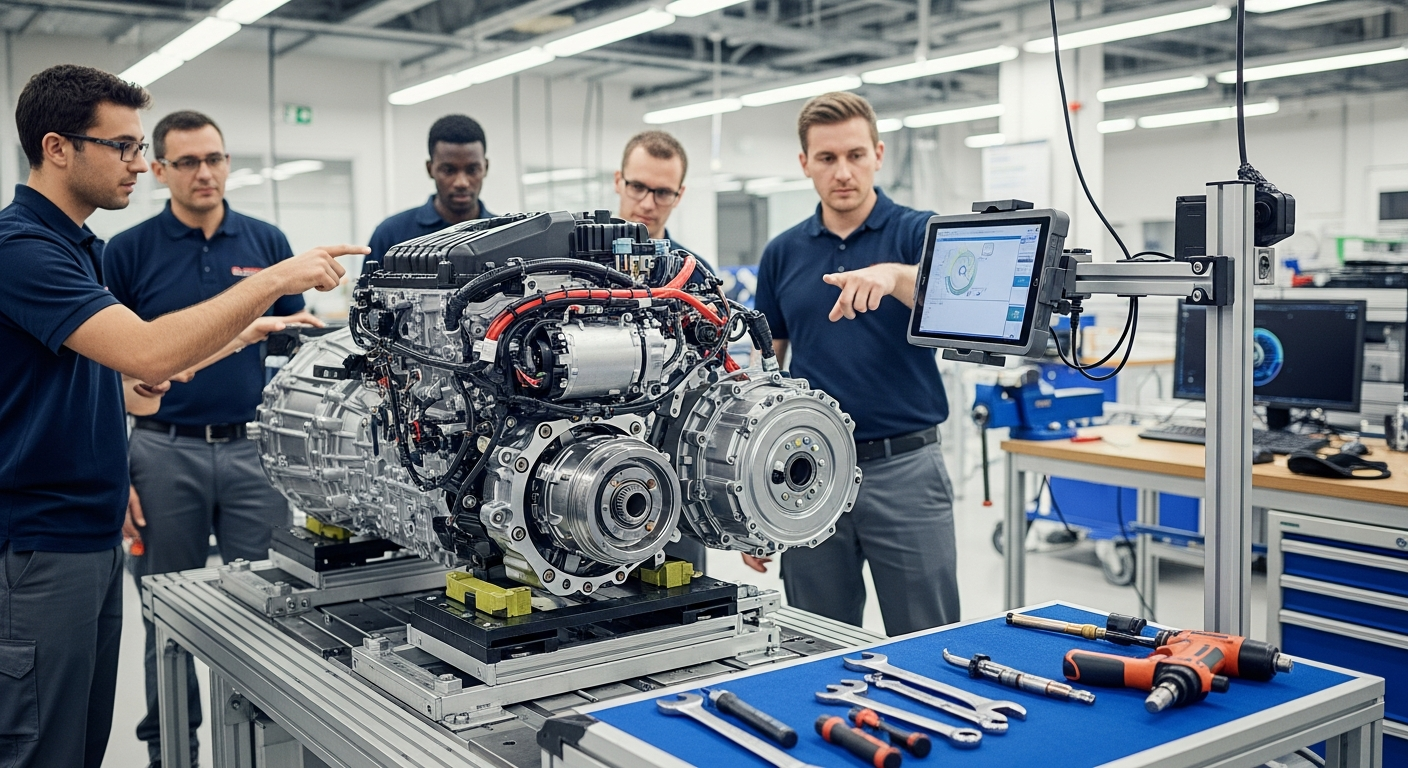
Understanding the Hybrid Electric Powertrain
At the core of any hybrid vehicle is its sophisticated powertrain, which seamlessly integrates an internal combustion engine with one or more electric motors. This technology allows the vehicle to operate in various modes, from purely electric at low speeds to a combination of both engine and electric power for acceleration or higher speeds. The primary goal is to optimize performance and fuel efficiency by leveraging the strengths of each power source. The electric motor provides instant torque, ideal for city driving and stop-and-go traffic, while the gasoline engine is more efficient for sustained highway speeds. This intricate dance between power sources is managed by an advanced control unit, which continuously assesses driving conditions and driver input to determine the most efficient power delivery strategy, showcasing remarkable innovation in automotive design.
Chassis Design and Vehicle Integration
The chassis of a hybrid vehicle is specifically engineered to accommodate the additional components required for its dual-power system, such as battery packs, power control units, and electric motors, without compromising mobility or passenger space. This often involves strategic placement of the battery pack, typically under the rear seats or in the trunk area, to maintain a balanced weight distribution and a low center of gravity. The overall design takes into account the added weight of these components, influencing suspension tuning and structural reinforcement. Effective vehicle integration ensures that all systems work harmoniously, contributing to the overall stability and handling characteristics crucial for safe transport and a comfortable ride.
Driving Dynamics and Energy Management
Hybrid driving dynamics are characterized by their sophisticated energy management systems. These systems intelligently switch between power sources, engage regenerative braking, and manage battery charging to maximize efficiency. When decelerating or braking, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy to recharge the battery, a process known as regenerative braking. This not only conserves energy but also reduces wear on the conventional brakes. The interplay between the engine and electric motor provides a smooth and responsive performance, adapting to various driving scenarios, from urban commutes to highway cruising. This continuous optimization is a testament to the technology’s focus on sustainability.
Advanced Safety Systems and Sensor Technology
Modern hybrid vehicles incorporate a wide array of advanced safety features, often leveraging sophisticated sensors and digital technology. These systems include adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, automatic emergency braking, and blind-spot monitoring, all designed to assist the driver and prevent accidents. The integration of radar, cameras, and ultrasonic sensors provides a comprehensive view of the vehicle’s surroundings, enhancing situational awareness. While fully autonomous driving is still evolving, many hybrids feature semi-autonomous capabilities that enhance safety and convenience, contributing to a more secure driving experience. These innovations continuously push the boundaries of automotive safety.
Maintenance Considerations for Hybrid Vehicles
Maintenance for hybrid vehicles shares many similarities with conventional cars but also includes specific considerations for their unique components. Regular checks of the engine’s oil and filters, tire rotations, and brake inspections remain essential. However, the electric drive system introduces new elements, such as the high-voltage battery pack and electric motor components. While these are generally designed for longevity, specific diagnostics and servicing may be required by trained technicians. Regenerative braking can extend the life of brake pads, but the conventional braking system still requires periodic inspection. Adhering to the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule is crucial for ensuring the long-term reliability and sustainability of the vehicle.
The Role of Tires and Braking Systems
The choice of tires plays a significant role in the overall efficiency and performance of a hybrid vehicle. Many hybrids are equipped with low rolling resistance tires designed to minimize friction and improve fuel economy. While these tires contribute to sustainability, they must still provide adequate grip and handling characteristics for safety. The braking system in a hybrid is a critical component, integrating both conventional hydraulic brakes and regenerative braking. The regenerative system handles much of the routine deceleration, converting kinetic energy back into electricity, which reduces wear on the physical brakes. However, the hydraulic brakes are essential for rapid stopping and emergency situations, requiring regular inspection to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Hybrid vehicle technology represents a dynamic field of automotive engineering that continues to evolve. By integrating internal combustion engines with electric powertrains, these vehicles offer a compelling balance of fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and robust performance. The ongoing innovation in design, safety features, and energy management systems underscores their role in the transition towards more sustainable transport solutions. Understanding these intricate mechanics provides insight into how hybrid vehicles contribute to a more efficient and environmentally conscious future for mobility.






